Second Congo War, The Most Deadliest War in Africa
In the First Congo War, the support of Rwanda and Uganda enabled Congolese rebel, Laurent Désiré-Kabila, to overthrow Mobutu Sese Seko's government. However, after Kabila was installed as the new President, he broke ties with Rwanda and Uganda. They retaliated by invading the Democratic Republic of the Congo, starting the Second Congo War. Within a few months, no less than nine African countries were involved in the conflict in the Congo, and by its end nearly 20 rebel groups were fighting in what had become one of the deadliest and most lucrative conflicts in recent history.
Following
Mobutu’s departure, Kabila assumed the presidency and restored the country’s
previous name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kabila initially was able to
attract foreign aid and provided some order and relief to the
country’s decimated economy. He also initiated the drafting of a new
constitution. The outward appearance of moving toward democracy conflicted with the reality of the situation:
Kabila held the bulk of power and did not tolerate criticism or opposition. Political parties and public
demonstrations were banned almost immediately following Kabila’s takeover of
the government, and his administration was accused of human rights abuse.
In
August 1998 the new leader himself was plagued by a rebellion in the country’s
eastern provinces—supported by some of Kabila’s former allies. The rebellion
marked the start of what became a devastating five-year civil war that drew in
several countries. By the end of 1998, the rebels, backed by the Ugandan and
Rwandan governments, controlled roughly one-third of the country. Kabila’s
government received support from the Angolan, Namibian, and Zimbabwean
governments in its fight against the rebels. A cease-fire and the deployment of
UN peacekeeping forces were among the provisions of the 1999 Lusaka Peace
Accord, an agreement intended to end the hostilities. Although it was
eventually signed by most parties involved in the conflict, the accord was not
fully implemented, and fighting continued. Meanwhile, long-standing
ethnic tensions between the Hema and the Lendu peoples erupted into violence in
the Ituri district in the eastern part of the country; this was further
complicated by rebel involvement and other political and economic factors,
spawning an additional conflict in a region already mired in the civil war.
Kabila
was assassinated in January 2001. He was succeeded by his son, Joseph, who
immediately declared his commitment to finding a peaceful end to the war. Soon
after Joseph Kabila assumed power, the Rwandan and Ugandan
governments and the rebels agreed to a UN-proposed pull-out plan, but it was
never fully actualized. Finally, in December 2002, an agreement reached in
Pretoria, South Africa, provided for the establishment of a
power-sharing transitional government and an end to the war; this agreement was
ratified in April 2003. A transitional constitution also was adopted that
month, and an interim government was inaugurated in July, with Kabila
as president. UN peacekeeping troops continued to maintain a presence in the
country.
Although
the civil war was technically over, the country was devastated. It was
estimated that more than three million people had been killed; those who
survived were left to struggle with homelessness, starvation, and disease. The
new government was fragile; the economy was in shambles; and societal infrastructure had been destroyed. With international
assistance, Kabila was able to make considerable progress toward reforming the
economy and began the work of rebuilding the country. However, his government
was not able to exercise any real control over much of the country; he had to
cope with fighting that remained in the east, as well as two failed coup attempts
in 2004. Nevertheless, a new, formal constitution was promulgated in 2006, and Kabila was victorious in
presidential elections held later that year.
In
January 2008 a peace agreement aimed at ending the fighting in the eastern part
of the country was signed by the government and more than 20 rebel groups. The
fragile truce was broken later that year when rebels led by Laurent Nkunda
renewed their attacks, displacing tens of thousands of residents and
international aid workers. In January 2009 Congolese and Rwandan troops
together launched an offensive against rebel groups in the east. They forced
Nkunda to flee across the border into Rwanda,
where he was arrested and indicted for war crimes by the Congolese government.
In May 2009 further efforts to resolve the continuing conflict in the east
included an amnesty extended to a number of militant groups there. Still,
violence in the east persisted, casting a pall on the celebrations of the
country’s 50th anniversary of independence in 2010.
The
country held presidential and parliamentary elections in November 2011. Eleven
candidates stood in the presidential race, with Kabila and former prime minister Étienne Tshisekedi being the front-runners. A January
2011 constitutional amendment had eliminated the second round of voting in
the presidential race, allowing for the possibility that a candidate might win
the presidency without the support of the majority of voters, a change that
many thought bolstered Kabila’s chances of reelection. Despite
problems with distributing electoral supplies to the country’s many remote
polling centres, the elections were held as scheduled on November 28. The
tallying of parliamentary results was expected to take several weeks, while the
tabulation of the presidential votes was expected to be completed in a week,
although it took slightly longer, as the process was hindered by the same
logistical obstacles that complicated the distribution of electoral supplies.
After two short delays in the release of the provisional results, Kabila was
declared the winner, with 49 percent of the vote; Tshisekedi followed, with 32
percent. The Supreme Court later confirmed the results, although several international
monitoring groups characterized the polls as being poorly organized and
noted many irregularities. Tshisekedi’s party rejected the results, and he
declared himself to be Congo’s rightful president; to that end, he had himself
sworn in as president on December 23, three days after Kabila’s official
inauguration had taken place. The tallying of the parliamentary election
results also took longer than expected. Results released in late January and
early February 2012 showed that more than 100 parties would be represented in
the National Assembly and that no one party had won a
majority. Kabila’s party and its allies, however, together had won slightly
more than half of the 500 seats.
With
Kabila’s presidential mandate set to expire at the end of 2016, there were
fears evident as early as 2013 that he would find a way to extend his time in
office, whether by modifying the constitution or by finding a reason to
postpone the next presidential election, and, fueled by such fears, many
protests were held. In 2015 Kabila’s administration proposed a series of
actions to precede the next elections, including conducting a census,
reorganizing the country’s administrative units (which would more than double
the number of provinces), and overhauling the voter registry, a task expected
to take more than a year to complete. Many thought that these actions
would delay the elections and ultimately extend Kabila’s term
in office by several years. Further stoking suspicions that he would not step
down as scheduled, in May 2016 the Constitutional Court ruled that if the polls
were delayed, Kabila could remain in office until a successor was elected. In
September the electoral commission formally requested that the Constitutional
Court allow for the 2016 presidential election to be postponed; the court ruled
in favour of the request the following month, which angered the opposition. A
crisis appeared to be averted, however, when a hard-wrought compromise deal was
signed by the government and most opposition groups on December 31. Its
provisions included allowing Kabila to remain president, but of a transitional
government with a prime minister selected from the opposition, until a new
president could be elected in 2017.
To
the consternation of many, the presidential election did not
occur as planned; it was eventually scheduled to take place on December 23,
2018, along with legislative, provincial, and local elections. In August 2018
Kabila’s spokesperson confirmed that Kabila would not be standing in the
presidential election. Instead, the candidate of the ruling party (the People’s
Party for Reconstruction and Democracy; PPRD) would be Emmanuel Ramazani Shadary, a former government minister and
provincial governor. Shadary was one of 21 approved presidential candidates.
Notable opposition figures Jean-Pierre Bemba and Moïse Katumbi were
not part of that group, as Bemba had been disqualified by the electoral
commission over International Criminal Court charges and Katumbi had been
blocked from returning to the country after time away and hence was not able to
register as a candidate by the deadline.
Although the opposition groups initially united to back Martin Fayulu as their candidate, protests from
supporters of Félix Tshisekedi—son of veteran opposition leader Étienne
Tshisekedi, who had died in 2017—led him to withdraw his support from Fayulu
and contest the election himself. Another opposition leader with broad
support, Vital Kamerhe, did the same.
Tensions
increased in the run-up to the elections, as evidenced by the violence
committed by security forces at political rallies and by the decision of Kinshasa’s governor
to ban campaign events in the city days before the scheduled polls. Ten days
before the elections were to be held, a mysterious fire destroyed thousands of
voting machines and other election materials in Kinshasa, an opposition stronghold.
Against this backdrop, there were concerns that peaceful, free, and fair
elections could not be held throughout the country. Indeed, just three days
before the scheduled date of the elections, the electoral commission announced
that it could not hold the elections as planned and hence was postponing them
until December 30. Shortly thereafter the electoral commission announced that
voting would be postponed until March in and around three cities—Beni, Butembo,
and Yumbi, all opposition strongholds—citing regional insecurity and an
outbreak of the Ebola virus disease as reasons for the delay. Given that
the next president was scheduled to be inaugurated in January, the postponement
effectively discounted the votes of the electorate in those areas, which
represented about 3 percent of all registered voters..
Elections
did take place on December 30 in the rest of the country. Although the voting
day was generally peaceful, there were complaints about the process, including
those about polling stations not opening on time or lacking necessary supplies,
as well as instances of voter intimidation and monitors being denied access
to polling stations and, later, vote-counting centres. When results were
released on January 10, Tshisekedi was announced the winner, with more than 38
percent of the vote; he was trailed by Fayulu, with almost 35 percent, and
Shadary, with almost 24 percent. The results, however, were counter to a
preelection poll and the observations of Congo’s Catholic bishops organization
(National Episcopal Conference of Congo; CENCO) election monitoring group, both
of which had Fayulu firmly in the lead. Fayulu and others alleged that Tshisekedi and Kabila had made a deal: an
election victory for Tshisekedi in exchange for Kabila and his associates
having their interests protected. Representatives of Kabila and Tshisekedi
denied the accusation.
Fayulu
challenged the results with the Constitutional Court. His argument was
bolstered by a trove of leaked election data as well as the results compiled by
CENCO, both of which showed him winning about 60 percent of the vote. The court
upheld Tshisekedi’s victory, however, and he was sworn in as president on
January 24, 2019. Against the backdrop of
lingering questions about the credibility of the election results, the day was
still significant, as Tshisekedi’s inauguration was the first peaceful transfer
of power in Congo since the country became independent in 1960.
1997-98
Tensions Build
When Kabila first became president of
the Democratic Repubilc of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda, who had helped bring him to
power, exerted considerable influence over him. Kabila appointed the Rwandan
officers and troops who had participated in the rebellion key positions within
the new Congolese army (the FAC), and for the first year, he pursued policies
in regard to the continued unrest in the eastern part of the DRC that were
consistent with Rwanda's aims.
The Rwandan soldiers were hated,
though, by many Congolese, and Kabila was constantly caught between angering
the international community, Congolese supporters, and his foreign backers.
On July 27, 1998, Kabila dealt with the situation by summarily calling for
all foreign soldiers to leave the Congo.
1998
Rwanda Invades
In a surprise radio announcement,
Kabila had cut his cord to Rwanda, and Rwanda responded by invading a week
later on August 2, 1998. With this move, the simmering conflict in the Congo
shifted into the Second Congo War.
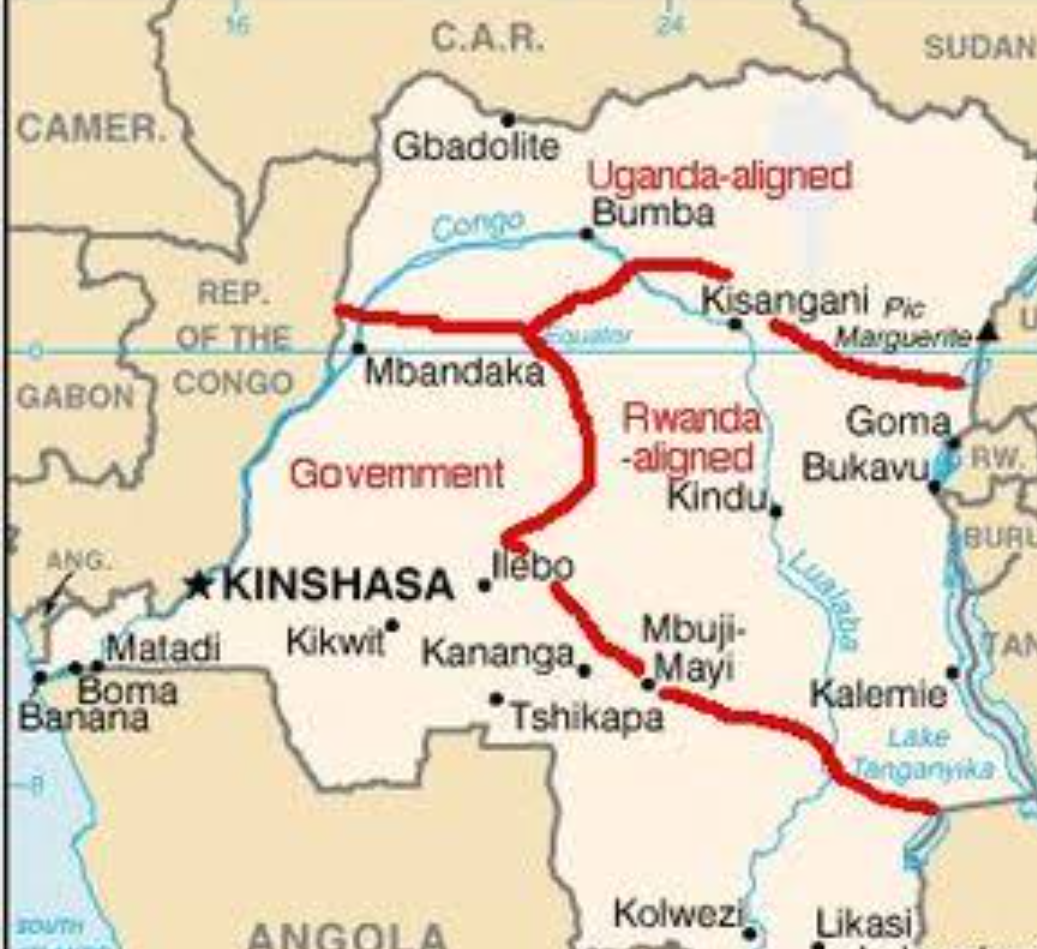
There were a number of factors driving
Rwanda's decision, but chief among them was the continued violence against
Tutsis within the eastern Congo. Many have also argued that Rwanda, one of the
most densely populated countries in Africa, harbored visions of claiming part
of the eastern Congo for itself, but they made no clear moves in this
direction. Rather they armed, supported, and advised a rebel group comprised
mainly of Congolese Tutsis, the Rassemblement Congolais pour la
Démocratie (RCD).
Kabila
saved (again) by foreign allies
Rwandan forces made quick strides in
eastern Congo, but rather than progress through the country, they tried to
simply oust Kabila by flying men and arms to an airport near the capital,
Kinshasa, in the far west part of the DRC, near the Atlantic ocean and taking
the capital that way.The plan had a chance of succeeding, but again, Kabila
received foreign aid. This time, it was Angola and Zimbabwe who came to his
defense. Zimbabwe was motivated by their recent investments in Congolese mines
and the contracts they had secured from Kabila's government.
Angola's involvement was more
political. Angola had been engaged in a civil war since decolonization
in 1975. The government feared that if Rwanda succeeded in ousting Kabila, the
DRC might again become a safe haven for UNITA troops, the armed opposition
group within Angola. Angola also hoped to secure influence over Kabila.
The intervention of Angola and
Zimbabwe was crucial. Between them, the three countries also managed to secure
aid in the form of arms and soldiers from Namibia, the Sudan (who was opposed
to Rwanda), Chad, and Libya.
Stalemate
With these combined forces, Kabila and
his allies were able to stop the Rwandan-backed assault on the capital. But the
Second Congo War merely entered a stalemate between countries that soon led to
profiteering as the war entered its next phase.